POLSTRACC / GW-LCYCLE / SALSA

Polar Stratosphere in a Changing ClimatePolar Stratosphere
in a Changing Climate
Gravity Wave Life Cycle
Seasonality of Air mass transport and origin
in the Lowermost Stratosphere using the HALO Aircraft
Mission status: Completed
Persons in Charge
Mission-PI
- Hermann Oelhaf (KIT)
- Björn-Martin Sinnhuber (KIT)
- Peter Hoor (Univ. Mainz)
- Andreas Engel (Univ. Frankfurt)
Contact point at DLR-FX for this mission:
HALO Project Management: Andreas Minikin
Postal address:
DLR Oberpfaffenhofen
Flugexperimente (FX)
Münchener Str. 20
82234 Weßling
Germany
Office phone:
+49 (0)8153 28-2538
HALO Deployment Base
HALO was operated from two bases during this campaign:
Time Period
Nov 2, 2015 – Mar 24, 2016
| Mission phase | Dates |
|---|---|
| Preparation incl. EMI testing | 2 Nov 2015 - 8 Dec 2015 |
| Mission Oberpfaffenhofen Phase 1 | 7 Dec 2015 - 21 Dec 2015 & 7 Jan 2016 - 11 Jan 2016 |
| Christmas break | 22 Dec 2015 - 6 Jan 2016 |
| Mission Kiruna Phase 1 | 12 Jan 2016 - 3 Feb 2016 |
| Break | 4 Feb 2016 - 22 Feb 2016 |
| Mission Kiruna Phase 2 | 23 Feb 2016 - 13 Mar 2016 |
| Mission Oberpfaffenhofen Phase 2 | 14 Mar 2016 - 20 Mar 2016 |
| Dismounting of payload | 21 Mar 2016 - 24 Mar 2016 |
Project description
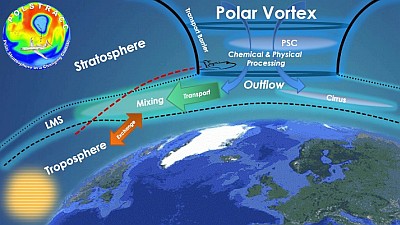
POLSTRACC. The HALO (High Altitude and LOng Range Research Aircraft) mission POLSTRACC will investigate the role of the Arctic upper troposphere and lower stratosphere (UTLS) in a changing climate.
The Arctic is the region that experiences the largest changes in Earth’s climate, with a rapid decline of Arctic sea ice, a strong warming of the surface atmosphere and changes in the chemistry and dynamics of the UTLS. In the Arctic stratosphere, large depletion of Arctic stratospheric ozone has been observed in recent cold winters, with still large uncertainties how this will respond to future climate change. Changes in the trace gas composition and cirrus cloud occurrence in the UTLS have a large impact on radiative forcing and surface climate. POLSTRACC aims at providing new scientific knowledge on the structure, composition and evolution of the Arctic UTLS. POLSTRACC will investigate chemical and physical processes involved in Arctic stratospheric ozone depletion, transport and mixing processes in the UTLS at high latitudes, polar stratospheric clouds and cirrus clouds. In contrast to previous Arctic aircraft campaigns, a specific focus is set on the Lowermost Stratosphere (LMS), a region where fast horizontal transport processes occur and which is particularly important for the atmospheric radiation budget. Utilizing the combination of field measurements and model simulations, POLSTRACC will help improving our understanding of the polar stratosphere in a changing climate.
POLSTRACC will be performed in four phases: Early winter flights will be performed from Oberfaffenhofen, Germany, in December 2015 with the aim to probe the early polar vortex (Oberpfaffenhofen 1). The main campaign phases will be based in Kiruna, Sweden, at 68°N with extensive flights inside and in the vicinity of the polar vortex at high latitudes. The activities in Kiruna will be split into two phases: from early January to early February 2016 (Kiruna 1) and from the end of February to mid of March 2016 (Kiruna 2). A final campaign phase based in Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany, in the mid of March 2016 (Oberpfaffenhofen 2) will provide the opportunity to study the remants of the dissipating polar vortex in mid-latitudes in spring.
The POLSTRACC activities are coordinated with the BMBF/ROMIC project GW-LCYLCE (Gravity Wave Life Cycle Experiment) and the SALSA project (Seasonality of Air mass transport and origin in the Lowermost Stratosphere using the HALO Aircraft), which will strongly enhance the scientific outreach and capabilities of the individual projects. POLSTRACC furthermore shares a similar payload with the HALO mission WISE (Wave-driven ISentropic Exchange), which addresses complementary scientific objectives.
GW-LCYCLE. The project GW-LCYCLE addresses the fundamental issue of internal gravity wave (IGW) excitation, propagation, and dissipation in the atmosphere. IGWs are one of the most important dynamical coupling processes between the troposphere and the middle atmosphere (10 to 120 km). IGWs couple different atmospheric regions both in the vertical as well as in the horizontal directions by means of momentum and energy transport. Notably, this coupling is effective both from the troposphere upwards, and also in the opposite direction by indirect effects on circulation patterns. While this importance of IGWs for understanding atmospheric structure, dynamics and climate is now widely recognized surprisingly little is still known about the details of the actual life cycle of IGWs.
GW-LCYCLE. The project GW-LCYCLE addresses the fundamental issue of internal gravity wave (IGW) excitation, propagation, and dissipation in the atmosphere. IGWs are one of the most important dynamical coupling processes between the troposphere and the middle atmosphere (10 to 120 km). IGWs couple different atmospheric regions both in the vertical as well as in the horizontal directions by means of momentum and energy transport. Notably, this coupling is effective both from the troposphere upwards, and also in the opposite direction by indirect effects on circulation patterns. While this importance of IGWs for understanding atmospheric structure, dynamics and climate is now widely recognized surprisingly little is still known about the details of the actual life cycle of IGWs.
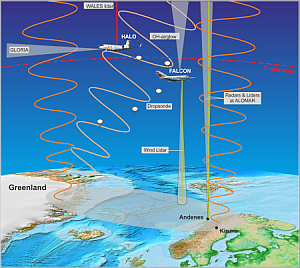
To address this issue, coordinated field campaigns deploying ground-based and airborne observations will be conducted. The results of these remote-sensing and in-situ measurement will be combined with state-of-the art numerical modelling as well as global observations of satellites.
Ground-based and airborne observation of IGW signatures will be conducted over Northern Scandinavia. The paths of the forecasted IGWs will be traced back to their likely source regions using ray tracing techniques. These source regions will then be verified experimentally using the airborne measurements involving two different aircraft, i.e., the DLR research aircraft FALCON and the German HALO research aircraft. Both aircraft will be operating at different altitudes around the tropopause to allow simultaneous gravity wave observations in the troposphere and stratosphere.
One of the key-instruments of the project is the Gimballed Limb Observer for Radiance Imaging of the Atmosphere (GLORIA). GLORIA is a novel instrument for infrared limb imaging of the atmosphere. Under cloud-free conditions, GLORIA measures temperature and a number of trace species at altitudes between 4 km and the flight altitude. For closed flight legs (e.g. as hexagons) 3D distributions can be retrieved with a spatial resolution better than 25 km in the horizontal and 500 m in the vertical. This allows the full characterization of single waves in terms of temperature amplitude and the 3D wave vector.
The combination of GLORIA observations with those of other in-situ and remote-sensing instruments (e.g. the airborne fast airglow imager FAIM) enables us to study the life cycle of IGWs from their source regions to their dissipation altitude. The combined results will then provide critical input to idealized numerical simulations using state of the art numerical models. The combined results will deliver constrains for gravity wave parameterizations which are needed to describe IGW effects in global circulation models.
SALSA. Background and objectives of SALSA (Seasonality of Air mass transport and origin in the Lowermost Stratosphere using the HALO Aircraft) are described in the TACTS/SALSA white paper. See link in section More information further below.
Partners
- Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT)
- Forschungszentrum Jülich (FZ Jülich)
- German Aerospace Center, Institute of Atmospheric Physics (DLR-IPA)
- Goethe University Frankfurt
- Heidelberg University
- Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz
- University of Wuppertal
Scientific instruments and payload configuration
List of scientific instruments for the mission:
| Scientific instrument acronym | Description | Principal investigator | Institution |
|---|---|---|---|
| GLORIA-AB | Gimballed Limb Observer for Radiance Imaging of the Atmosphere | Felix Friedl-Vallon Peter Preuße | KIT FZ Jülich |
| WALES | Water Vapour Differential Absorption Lidar | Andreas Fix, Martin Wirth | DLR-IPA |
| FISH | Fast In-situ Stratospheric Hygrometer | Martina Krämer | FZ Jülich |
| HAI | Hygrometer for Atmospheric Investigations | Volker Ebert, Bernhard Buchholz | PTB (National Metrology Institute) |
| FAIRO | Fast Ozone Measurement | Andreas Zahn | KIT |
| AENEAS | NOY measurement | Helmut Ziereis | DLR-IPA |
| AIMS | Atmospheric Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometer | Christiane Voigt, Tina Jurkat | DLR-IPA |
| TRIHOP | Peter Hoor, Heiko Bozem | Univ. Mainz | |
| HAGAR-V | High Altitude Gas AnalyzeR | Michael Volk | Univ. Wuppertal |
| GhOST | Gaschromatograph for Observation of Stratospheric Tracers | Andreas Engel, Harald Bönisch | Univ. Frankfurt |
| Dropsonde system | Meteorological Dropsondes | Stefan Kaufmann | DLR-IPA |
| miniDOAS | Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy | Klaus Pfeilsticker | Univ. Heidelberg |
| BAHAMAS | HALO basic data acquisition system | Andreas Giez | DLR-FX |
Cabin and exterior configuration of HALO for the mission
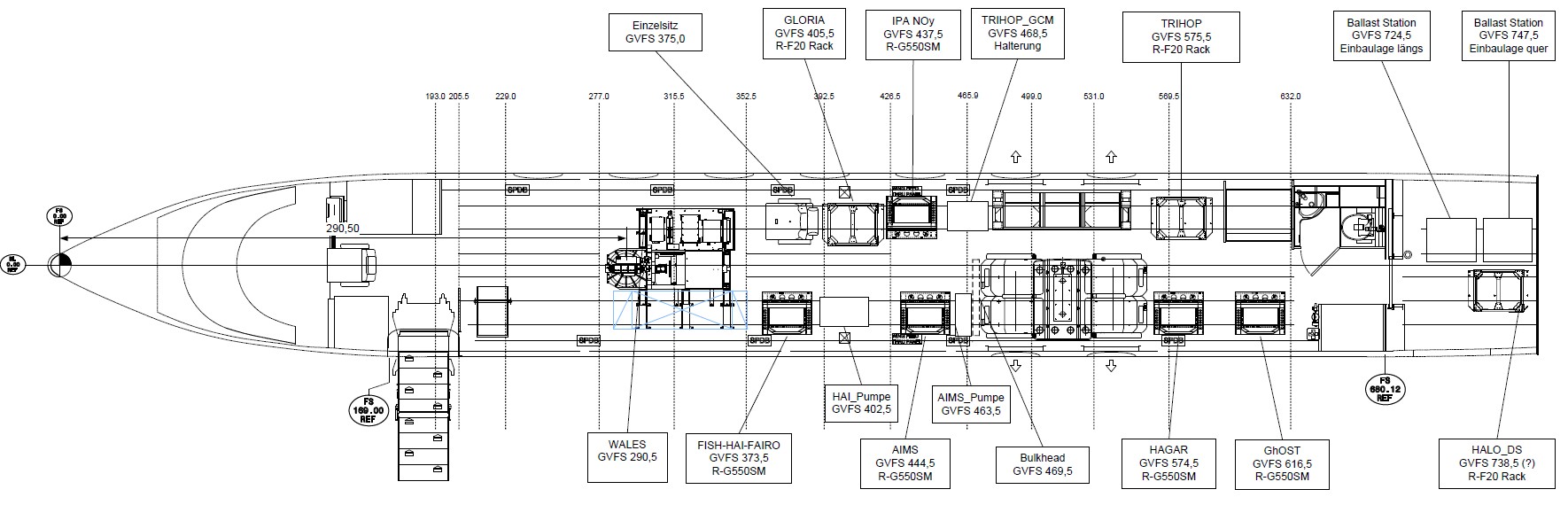
HALO cabin layout for POLSTRACC
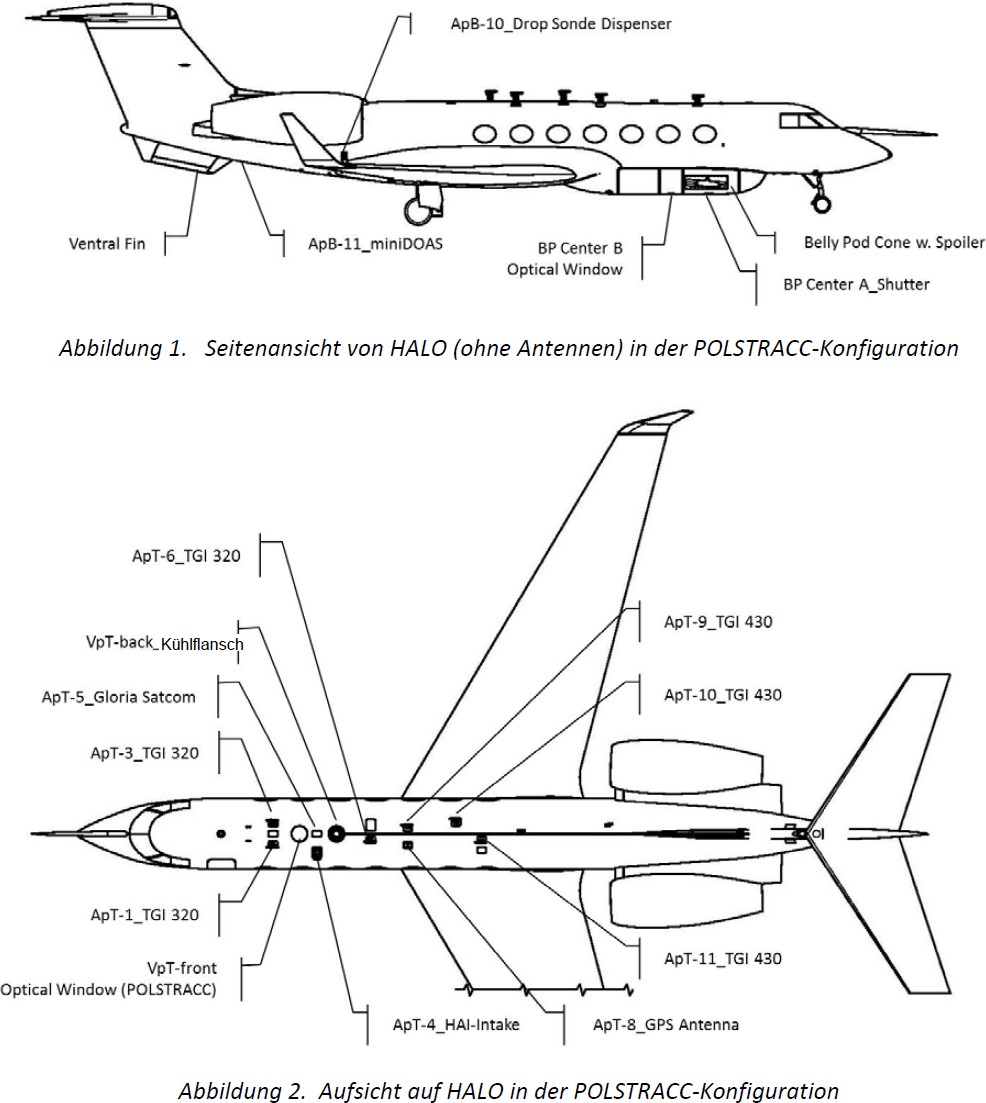
HALO exterior configuration for POLSTRACC
Halo flights for this mission
| Aircraft registration | Date | Take off - Landing / UT | Total flight time / h | From - To | Mission # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-ADLR | 2015-03-04 | 11:10:00 -13:45:00 | 2.58 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-03-06 | 09:25:00 - 10:45:00 | 1.33 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-03-09 | 09:55:00 - 12:00:00 | 2.08 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-03-10 | 08:20:00 - 10:55:00 | 2.58 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-03-12 | 09:15:00 - 11:50:00 | 2.58 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-03-13 | 11:15:00 - 13:05:00 | 1.83 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-03-23 | 14:35:00 - 16:25:00 | 1.83 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-03-24 | 08:55:00 - 09:35:00 | 0.67 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-03-24 | 12:40:00 - 15:40:00 | 3.00 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-03-25 | 09:55:00 - 12:20:00 | 2.42 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-04-07 | 09:25:00 - 11:00:00 | 1.58 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-04-07 | 14:20:00 - 16:10:00 | 1.83 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-04-08 | 06:00:00 - 06:40:00 | 0.67 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-04-15 | 05:40:00 - 07:40:00 | 2.00 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test |
| D-ADLR | 2015-12-08 | 14:10:00 - 16:45:00 | 2.58 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test 1 |
| D-ADLR | 2015-12-13 | 08:00:00 - 11:10:00 | 3.17 | EDMO - EDMO | Flight test 3 |
| D-ADLR | 2015-12-17 | 12:45:00 - 21:00:00 | 8.25 | EDMO - EDMO | Mission flight 4 |
| D-ADLR | 2015-12-21 | 07:50:00 - 17:35:00 | 9.75 | EDMO - EDMO | Mission flight 5 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-01-12 | 07:55:00 - 16:50:00 | 8.92 | EDMO - ESNQ | Mission flight 6 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-01-18 | 09:34:00 - 14:30:00 | 4.93 | ESNQ - ESNQ | Mission flight 7 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-01-20 | 11:06:00 - 19:53:00 | 8.78 | ESNQ - ESNQ | Mission flight 8 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-01-22 | 09:29:00 - 17:45:00 | 8.27 | ESNQ - ESNQ | Mission flight 9 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-01-25 | 06:43:00 - 13:29:00 | 6.77 | ESNQ - ESNQ | Mission flight 10 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-01-28 | 16:16:00 - 23:01:00 | 6.75 | ESNQ - ESNQ | Mission flight 11 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-01-31 | 05:55:00 - 15:02:00 | 9.12 | ESNQ - ESNQ | Mission flight 12 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-02-02 | 15:22:00 - 22:45:00 | 7.38 | ESNQ - ESNQ | Mission flight 13 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-02-26 | 11:19:00 - 20:59:00 | 9.67 | ESNQ - ESNQ | Mission flight 14 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-02-29 | 02:56:00 - 10:16:00 | 7.33 | ESNQ - ESNQ | Mission flight 15 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-06 | 05:05:00 - 13:38:00 | 8.55 | ESNQ - BIKF | Mission flight 16 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-06 | 14:26:00 - 17:09:00 | 2.72 | BIKF - ESNQ | Mission flight 16 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-09 | 07:46:00 - 14:04:00 | 6.30 | ESNQ - BGSF | Mission flight 17 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-09 | 14:41:00 - 18:14:00 | 3.55 | BGSF - ESNQ | Mission flight 17 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-10 | 15:02:00 - 22:56:00 | 7.90 | ESNQ - ESNQ | Mission flight 18 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-13 | 07:08:00 - 12:14:00 | 5.10 | ESNQ - BGSF | Mission flight 19 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-13 | 13:15:00 - 18:28:00 | 5.22 | BGSF - EDMO | Mission flight 19 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-16 | 09:18:00 - 16:02:00 | 6.73 | EDMO - LPFR | Mission flight 20 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-16 | 16:42:00 - 19:25:00 | 2.72 | LPFR - EDMO | Mission flight 20 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-18 | 09:26:00 - 14:02:00 | 4.60 | EDMO - ESNQ | Mission flight 21 |
| D-ADLR | 2016-03-18 | 14:39:00 - 17:56:00 | 3.28 | ESNQ - EDMO | Mission flight 21 |
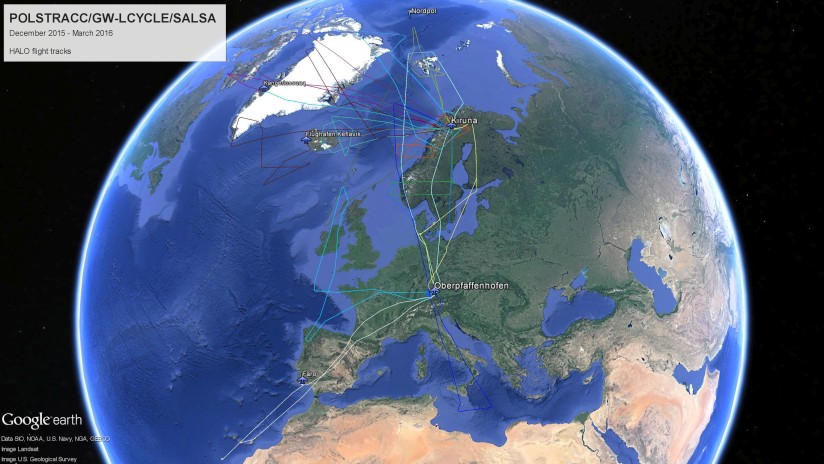
HALO flight tracks
More information
Scientific background and links to more information
-
- POLSTRACC homepage and wiki (including White Paper): [more..]
- GW-LYCLE as part of the ROMIC project: [more..]
-
SALSA White Paper: [pdf document..]
Campaign reports and stories
-
- Campaign news: [more..]
- Blog by Isabell Krisch: Campaign blog
- Blog by Jens Krause: POLSTRACC 2015/2016
Press releases, media etc
Press release KIT (11-Feb-2016):
Messkampagne POLSTRACC: Starker Ozonabbau über der Arktis möglich
Press release Forschungszentrum Jülich (5-Jan-2016):
Mit HALO zum Nordpol
Press release KIT (10-Dec-2015):
Ozon und Klima: Mit dem Forschungsflugzeug HALO zum Nordpol
Press release DLR (10-Dec-2015):
Forschungsflugzeug HALO: Klimaforschung in arktischen Höhen
Publications
Obersteiner, F., Bönisch, H., Keber, T., O’Doherty, S., and Engel, A.: A versatile, refrigerant- and cryogen-free cryofocusing–thermodesorption unit for preconcentration of traces gases in air, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 9, 5265-5279, doi:10.5194/amt-9-5265-2016, 2016.
